Computer Vision
Computer vision is transforming the way we interact with technology. From self-driving cars and medical imaging to retail and entertainment, computer vision enables machines to "see" and interpret the world around us, opening doors to innovations once confined to science fiction.
What is Computer Vision?
At its core, computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that trains computers to interpret and understand the visual world. By processing digital images and videos, computer vision systems can identify objects, track movement, and even make decisions based on visual input. This technology relies on a combination of machine learning, deep learning, and data processing techniques to analyze pixels and detect patterns that are too complex for traditional algorithms.
Brief History
The evolution of computer vision began decades ago, when researchers first attempted to create algorithms that could perform basic image processing tasks. Early methods focused on simple operations like edge detection and shape recognition. However, as computational power increased and more sophisticated algorithms emerged, computer vision made a leap forward. The advent of deep learning in the last decade—especially through convolutional neural networks (CNNs)—has been pivotal, enabling significant advancements in image classification, object detection, and even facial recognition.
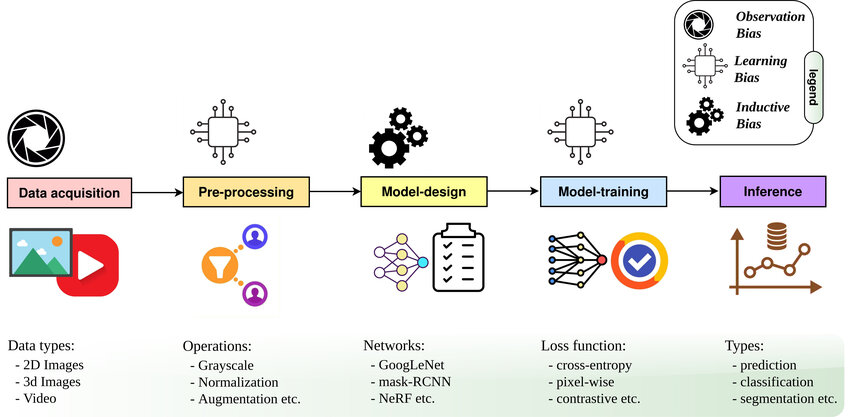
How Computer Vision Works
Modern computer vision systems operate through several key steps:
- Data Acquisition: This is the process of capturing images or videos using cameras or sensors. The quality of input data can greatly affect the performance of a vision system.
- Pre-processing: Before any analysis can occur, images are often cleaned up. Techniques like noise reduction, contrast enhancement, and normalization ensure that the data is in the best possible form for analysis.
- Model-design (Feature Extraction): The system identifies key features within the image—edges, textures, and colors—that help in recognizing objects or patterns.
- Model-training: Using vast datasets, computer vision algorithms learn to associate specific features with particular objects or scenarios. This training phase is critical for accuracy.
- Inference: Once the model is trained, it can be deployed to analyze new images, detecting and classifying objects in real-time.
Diverse Applications of Computer Vision
The potential applications of computer vision are vast and varied:
- Self-Driving Cars: Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on computer vision to interpret their surroundings. Cameras and sensors capture data, which is processed in real-time to detect pedestrians, traffic signs, and other vehicles, ensuring safe navigation on the roads.
- Healthcare and Medical Imaging: In medicine, computer vision aids in diagnosing diseases by analyzing medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Algorithms can detect subtle anomalies that might be missed by the human eye, leading to early diagnosis and improved treatment outcomes.
- Retail and E-Commerce: Retailers are increasingly using computer vision to enhance the customer experience. From automated checkout systems that recognize products to personalized shopping experiences, vision technology helps bridge the gap between physical and digital retail.
- Security and Surveillance: Facial recognition and motion detection systems are becoming staples in security. Computer vision enables real-time monitoring, ensuring that any unusual activity is quickly identified and addressed.
- Agriculture: Farmers use computer vision to monitor crop health, detect pests, and optimize harvesting. Drones equipped with cameras survey large fields, while algorithms analyze the images to provide actionable insights, helping to improve yield and reduce waste.
Challenges in Computer Vision
While the progress in computer vision is impressive, several challenges remain:
- Data Quality and Quantity: Training robust computer vision models requires large amounts of high-quality data. In many cases, obtaining such datasets can be challenging.
- Real-Time Processing: For applications like autonomous driving, processing visual data in real-time is crucial. This demands powerful hardware and efficient algorithms.
- Bias and Fairness: As with many AI systems, computer vision models can inadvertently learn and propagate biases present in their training data. Ensuring fairness and accuracy remains a significant area of research.
- Privacy Concerns: The widespread deployment of vision-based surveillance raises important questions about privacy and data security. Balancing innovation with ethical considerations is a key concern for developers and policymakers alike.
The Future of Computer Vision
Looking ahead, the future of computer vision is both exciting and full of potential. Researchers are exploring ways to improve model accuracy, reduce processing times, and apply vision technology in new fields such as augmented reality (AR) and robotics. As computing power continues to grow and algorithms become more sophisticated, we can expect computer vision to further blur the line between human and machine perception.
Innovations like edge computing—where data is processed closer to where it is captured—are set to revolutionize industries by reducing latency and increasing the efficiency of real-time applications. Moreover, the integration of computer vision with other AI disciplines, such as natural language processing and reinforcement learning, promises to unlock new levels of machine intelligence.
Conclussion
Computer vision is not just about making machines see—it’s about empowering technology to understand and interact with the world in a way that enhances human capabilities. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, the impact of computer vision will undoubtedly be felt across every facet of our lives. Whether it’s improving safety on our roads, revolutionizing healthcare, or transforming the retail experience, computer vision stands as a testament to the remarkable progress in artificial intelligence and the endless possibilities of technology.

